Surface and Deep Processing: Cognitive Behaviors of Aha! Moments (Part II)
This article is a continuation of a research entry from the May 24, 2021 edition:
The spectrum of early research on insight ranges from observing changes in behavior and understanding psychological patterns that influence learning (Bühler, 1907; Duncker & Lee, 1945; Wallas, 1926), to the present and how insight is a unique form of learning. There are a number of theories on insight; at present, no one theory dominates interpretation (Kounios & Beeman, 2015; Sternberg 1996). In spite of differences between theories, they share two principles: (a) sudden, conscious change in a person’s representation of a stimulus, situation, event, or problem (Davidson, 1995; Kaplan & Simon, 1990), and (b) the change occurs unexpectedly (Jung-Beeman, et al., 2004; Kounios & Beeman, 2014; Metcalfe, 1986). Further, a strong correlation has been demonstrated between moments of insight and increased engagement in learning, positive boost in mood, and greater likelihood of more moments of insight (Kizilirmak, Da Silva, Imamoglu, & Richardson-Klavehn, 2016; Kounios & Beeman, 2014). Aha! moments have been shown to increase and enhance memory performance (Ash, Jee, & Wiley, 2012; Auble, Franks, & Soraci, 1979; Danek, Fraps, von Müller, Grothe, & Öllinger, 2013; Dominowski & Buyer, 2000; Kizilirmak, Da Silva, Imamoglu, & Richardson- Klavehn, 2016), reliably grounded on insight’s proven ability to, “comprise associative novelty, schema, congruency, and intrinsic reward” (Kizilirmak et al., 2016, p. 1).
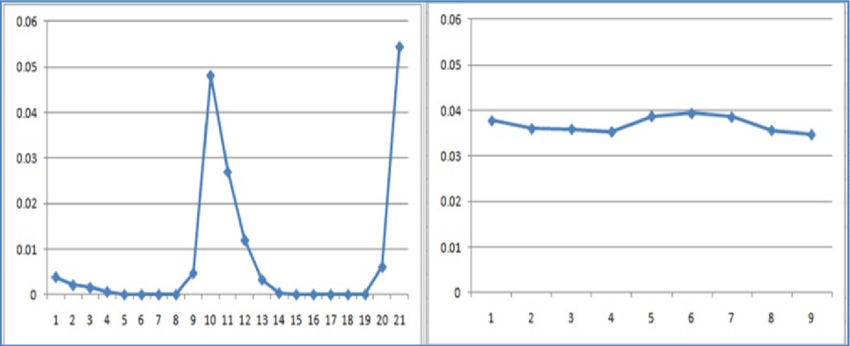
The observation and categorization of these moments can also be a source of valuable information for theorists and educators. Crocker and Algina (1986) demonstrate this operationalization in order to, “establish some rule of correspondence between the theoretical construct and observable behaviors that are legitimate indicators” (p. 4). The suddenness of Aha! moments makes observing behavioral changes (and subsequent changes in understanding) more dramatic and pronounced, as opposed to more gradual and deductively reasoned outcomes. Baker, Goldstein, and Heffernan (2010) have observed this distinction by studying the precise moment when understanding changes – graphing the precise moment of learning in humans. Baker et al. (2010) diagram the shift in surface to deep processing by showing the, “differences between gradual learning (such as strengthening of a memory association) and learning given to ‘eureka’ moments, where a knowledge component is understood suddenly” (p. 13).
Figure 5. A Single Student’s Performance on a Specific Knowledge Concept (Baker et al., 2010, p. 13)
Baker et al. explain that, “entering a common multiple” (left, Figure 5) results in a “spiky” graph, indicating eureka learning, while “identifying the converted value in the problem statement of a scaling problem” (right, Figure 5) results in a relatively smooth graph, indicating more gradual learning (p. 14).
Another important implication to consider is that deep processing seems to create greater investment in learning, along with more positive outcomes for students. Dolmans, Loyens, Marcq, and Gijbels (2016) have reviewed 21 different studies that reported on surface and deep processing strategies in relation to problem-based learning, and concluded that students using deep processing strategies use, “the freedom to select their own resources to answer the learning issues, which gives them ownership over their learning” (p. 1097). This ownership suggests a strong link between intrinsic and autonomous motivation, resulting in stronger and longer-lasting outcomes. Dolmans et al. also report that surface learning strategies with problem-based learning had a similar negative effect, stating:
a high perceived workload will more likely result in surface approaches to studying and might be detrimental for deep learning. Students who perceive the workload as high in their learning environment are more likely to display a lack of interest in their studies as well as exhaustion. This is particularly true for beginning [problem-based learning] students. (p. 1097)
““If we get the deep processing, we almost always get the surface, but with much richer and rewarding outcomes!””
The meta-analysis concluded by affirming these positive deep processing outcomes do not come at the cost of the various surface processing benefits (p. 1097). Deep processing strategies employed by learners have also been shown to boost long-term recall of information and wider conceptual understanding. Jensen, McDaniel, Woodard, and Kummer (2014) report that learners who utilized deep processing learning strategies while preparing for high-level assessments (i.e., problem solving, analysis, and evaluation) performed better than students that did not, and these students retained a, “deep conceptual understanding of the material and better memory for the course information” (p. 307). Jensen et al. (2014) have found that this higher level of cognitive processing and understanding also made transfer-appropriate processing more likely. This conclusion is supported by similar research conducted on learners using deep processing strategies and motivated by deeper conceptual understanding (Carpenter, 2012; Fisher & Craik, 1977; McDaniel, Friedman, & Bourne, 1978; McDaniel, Thomas, Agarwal, McDermott, & Roediger, 2013). Students using transfer-appropriate processing outcomes showed improved mastery and conceptual development greater than surface strategies and beyond the at-hand assessment; the gains were greater in current work and also in future assessments utilizing deep processing strategies. This developed processing strategy offers learners the greatest advantage in future outcomes. Studying Aha! moments in learning makes understanding surface processing and shifts into deep processing more probable, and the transfer-appropriate advantages more common, offering teachers a tremendous perspective into how to best develop pedagogy.